Formula
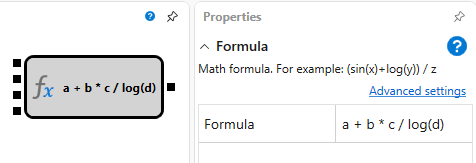
A cube is used to calculate a mathematical formula with an arbitrary number of arguments. You can choose a formula from the available list or write your own. In the case of writing your own formula, the number of incoming sockets is determined automatically.
Incoming sockets
- Value – the value with which you can perform mathematical operations (for example, a number or indicator). The number of input values depends on the formula.
Outgoing sockets
- Result – calculated value of the mathematical formula.
Parameters
- Formula – predefined set of mathematical formulas.
Together with the standard mathematical operators, you can use the following functions:
- abs(a) - returns the absolute value of a number.
- acos(a) - returns the angle which cosine is equal to the specified number.
- asin(a) - returns the angle which sine is equal to the specified number.
- atan(a) - returns the angle which tangent is equal to the specified number.
- ceiling(a) - returns the smallest integer that is greater than or equal to a specified number.
- cos(a) - returns the cosine of the specified angle.
- exp(a) - returns the value of e raised to the specified power.
- floor(a) - returns the largest integer that is less than or equal to the specified number.
- log(a) - returns the natural logarithm (with base e) of the specified number.
- log10(a) - returns the logarithm with base 10 of the specified number.
- max(a, b) - returns the larger of two decimal numbers.
- min(a, b) - returns the smaller of two decimal numbers.
- pow(a, b) - returns the specified number raised to the specified power.
- sign(a) - returns an integer indicating the sign of the specified number.
- sin(a) - returns the sine of the specified angle.
- sqrt(a) - returns the square root of the specified number.
- tan(a) - returns the tangent of the specified angle.
- truncate(a) - calculates the integer part of the specified number.